Explain Difference Between Crude Rates and Adjusted Rates
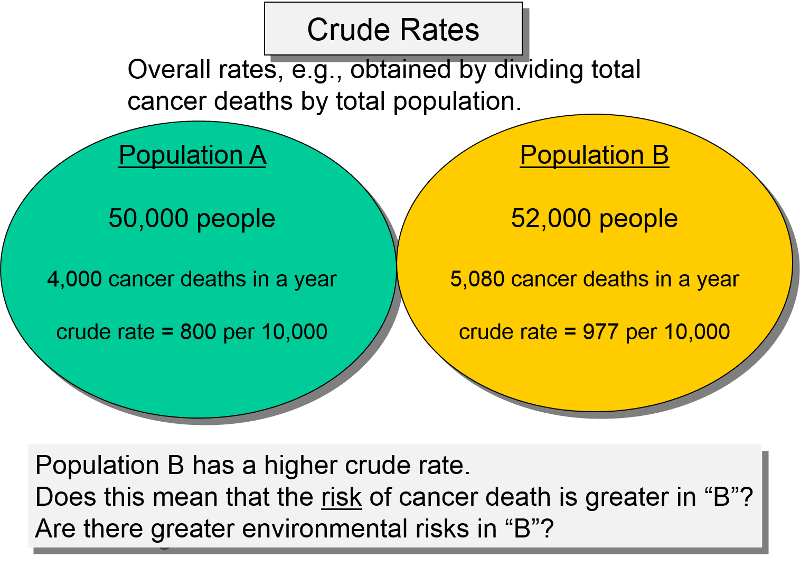
Crude Specific and Adjusted Rates EPI A summary measure calculated by dividing the total number of cases in the population by the total number of individuals in that population at a specified time period. Calculate the crude mortality rates for Population A and Population B.
Age-adjusted rates published elsewhere eg in the annual Missouri Vital Statistics may be slightly different from those found in the MICAs or Community Data Profiles due to updating of population estimates for years between decennial CensusesThe constant or per population number used for the age-adjusted rates may vary depending on the type of event.

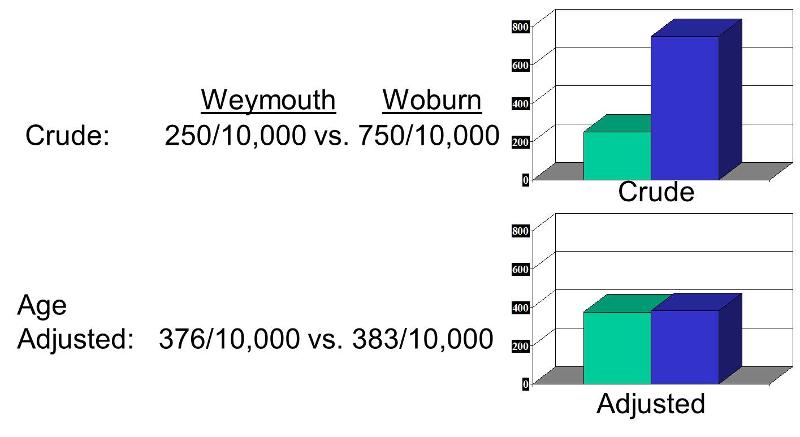
. For determining whether a significant difference exists between two crude non-adjusted rates or whether the difference between them is due to random effects. What makes the crude rates different is that older people have a higher risk of cancer mortality and population B has a greater proportion of older people. When the two crude rates are dependent ie rates from overlapping time periods such as 1960 to 1970 and 1965 to 1975 or.
Age groups that cover a large range of ages such as adults ages 18-64 may be age-adjusted Age-adjusted Rates. Calculate the age-specific mortality rates for Population A and Population B. Age-adjusted rates are those used to make comparisons across groups and over time when groups differ in age structure.
Crude specific and adjusted rates. Where B Total No. 1074 652 422 San Jose Males.
If it is. Epidemiological rates may be crude specific or adjusted standardized. Even if two states have the same age-adjusted rates the state with the relatively older population generally will have higher crude rates because incidence or death rates for most cancers increase with age.
P Mid year population of the year B P Crude Birth rate 1000. If the rates are calculated. Note that although the crude rate for community A was larger than that for community B the ADR for community A is smaller than.
A crude death rate is a ratio of deaths during a year applied to the total mid-year population eg. You just studied 7 terms. In other words the age-specific rates are the same but the higher proportion of older people in population B means that the overall crude rate is more heavily weighted by the age-specific rate among older people.
In this step we are calculating the crude age. Crude rates are reported in the Community Data Profiles for birth pregnancy and WIC indicators. Calculate the crude and age adjusted rate ratios for Population A compared to Population B.
Explain in your own words the difference between crude and age-standardized or age-adjusted mortality rates. 650 1176 -526 San Jose Females. Crude Rate -Age Adjusted Rate Rate Difference San Fran Males.
Specific rates differentiate cases and populations by cause age sex race or other factors. 16 Adjusted rates account for the differences in characteristics between populations and ensure that any observed variations in the measured rates are not a result of the heterogeneity of the. As with any summary measure adjusted rates may hide great differences between groups which can be of importance to explain changes in the rates due to or associated with the variable that we wish to adjust for for example.
Age adjusting rates allows. If you look at any of the states listed on Table 1 the values of crude mortality rate and age-adjusted mortality rate are different. 536 697 -161 I interpreted this as San Jose males had the greatest rate difference between crude death rate and age-adjusted rate.
The term mortality refers to the condition that one day one will have to die. Explain the difference between the crude and age adjusted rate ratio what could explain the difference. Of live births in a given year area.
3489 heart disease deaths per 100000 population in 1997. Rates for specific age groups such as infants under the age of 1 or adults ages 20-24 are also crude rates unless otherwise specified. Thus the ADR for community A is 42 deaths per 1000 population and the ADR for community B is 52 per 1000.
The main difference between a crude odds ratio and an adjusted odds ratio is that the adjusted odds ratio is adjusted according to the other variables within a model. Crude rates are influenced by the underlying age distribution of the states or other localitys population. For example all animals will eventually die one day.
Why are age standardized mortality rates aka age-adjusted mortality rates necessary. 19 rows Step 2. Crude rates can be misleading when populations differ in age structure or by some other attribute Crude birth rates are higher in younger populations and crude death rates are higher in older populations.
Crude rates use the total number of disease cases and the entire population in their calculations. Please download our Microsoft Excel file to calculate Age-Adjusted Rates XLS. Adjusted rates allow for the comparison.
Nevertheless whenever possible it is important to analyze the specific rates along with the adjusted rates. If the difference is 10 or greater we conclude that there was confounding. Crude Birth Rate CBR Ratio of the total number of live birth to the average population ever lived during a given year and geographical area.
Why are age-standardized mortality rates aka age-adjusted mortality rates necessary. Crude Rates vs. The populations must be for the same geographic area sex race and years the sum of the black female populations for 2000-2004 in the SEER 9 registries.
Age and sex are two of the most common variables used for standardization and they are called standardized rates. The difference between crude rates and standardized rates is that crude rates are calculated based on the population under study as a whole whereas standardized rates are based on particular characteristics as standard Figure 1. Next we use population data with the counts to calculate crude rates for each of the 19 age groups.
The magnitude of confounding is the percent difference between the crude and adjusted measures of association calculated as follows for either a risk ratio or an odds ratio. 1245 1120 125 San Fran Females. As with crude rates the ADR is usually expressed in terms of a rate per 1000 or per 100000 population.
Explain the difference between crude and age-standardized or age-adjusted mortality rates.

Adjusted Rates Nancy D Barker Adjusted Rates Crude Rates Table Ppt Download

Adjusted Rates Nancy D Barker Adjusted Rates Crude Rates Table Ppt Download
0 Response to "Explain Difference Between Crude Rates and Adjusted Rates"
Post a Comment